본 게시물은 Java 언어로 배우는 디자인 패턴 입문 - Yuki Hiroshi 저를 기반으로 공부한 것을 정리하며 Typescript로 재작성해본 내용입니다.
Strategy 패턴이란 ?
Strategy란 전략을 의미한다.
모든 프로그램은 문제를 해결하기 위해 작성되며 문제를 해결하기 위한 알고리즘들이 구현되고 있다.
Strategy 패턴은 그 알고리즘을 모두 교환 할 수 있으며,
빈틈없이 교체하여 같은 문제를 다른 방법으로도 쉽게 해결할 수 있도록 도와주는 패턴이다.
예제 프로그램
작성할 예제 프로그램은 "가위바위보"를 실행하는 프로그램이다.
가위바위보에 대한 전략으로 랜덤 전략, 이기면 같은 것을 내는 전략을 구현할 것이다.
| 이름 | 해설 |
|---|---|
| Hand | 가위바위보의 '손'을 표시하는 클래스 |
| Strategy | 가위바위보의 '전략'을 표시하는 인터페이스 |
| WinningStrategy | 이기면 다음에도 같은 손을 내는 전략을 표시하는 클래스 |
| RandomStrategy | 랜덤으로 손을 내는 전략을 표시하는 클래스 |
| Player | 가위바위보를 하는 플레이어를 표시하는 클래스 |
| Main | 동작 테스트용 메소드 |
Hand 클래스
export class Hand {
public static readonly HANDVALUE_MUK: number = 0; // 주먹
public static readonly HANDVALUE_CHI: number = 1; // 가위
public static readonly HANDVALUE_PAA: number = 2; // 보
public static readonly hand = [
new Hand(Hand.HANDVALUE_MUK),
new Hand(Hand.HANDVALUE_CHI),
new Hand(Hand.HANDVALUE_PAA),
]; // static method에서 this를 호출할 수 없다
private static readonly nameList: string[] = ['주먹', '가위', '보'];
private handValue: number;
constructor(handValue: number) {
this.handValue = handValue;
}
public static getHand = (handValue: number): Hand => {
return Hand.hand[handValue];
};
public isStrongerThan = (h: Hand): boolean => {
return this.fight(h) === 1;
};
public isWeakerThan = (h: Hand): boolean => {
return this.fight(h) === -1;
};
private fight = (h: Hand): number => {
if (this === h) return 0;
else if ((this.handValue + 1) % 3 === h.handValue) return 1;
else return -1;
};
public toString = (): string => {
return Hand.nameList[this.handValue];
};
}
Hand 클래스는 가위바위보의 '손'을 표시하는 클래스이며 0은 주먹, 1은 가위, 2는 보로 표현한다.
Hand 클래스의 인스턴스는 세 개만 작성되고, 처음에 세 개의 인스턴스가 만들어져 배열 hand에 저장된다.
getHand 메소드를 이용해 인스턴스를 얻을 수 있다.
손의 값을 인수로 할당하면 인스턴스가 반환되며 이는 "Singleton" 패턴의 일종이다.
isStrongerThan, isWeakerThan은 손의 승패를 비교하는 메소드이다.
이 Hand 클래스는 다른 클래스에서 사용되지만 Strategy 패턴의 역할에는 포함되지 않는다.
Strategy 인터페이스
export interface Strategy {
nextHand: () => Hand;
study: (win: boolean) => void;
}
Strategy 인터페이스는 가위바위보의 전략을 위한 추상 메소드의 집합이다.
nextHand는 '다음에 내는 손을 얻기' 위한 메소드, study는 '직전에 낸 손으로 이겼는지, 졌는지'를 학습하기 위한 메소드이다.
WinningStrategy 클래스
export class WinningStrategy implements Strategy {
private won: boolean = false;
private prevHand: Hand;
public nextHand = (): Hand => {
if (!this.won) {
this.prevHand = Hand.getHand(Math.floor(Math.random() * 3));
}
return this.prevHand;
};
public study = (win: boolean): void => {
this.won = win;
};
}
WinningStrategy 클래스는 Strategy 인터페이스를 구현하는 클래스 중 하나이다.
이 클래스는 직전 승부에서 이겼으면 다음에도 같은 손을 낸다는 전략을 취한다.
RandomStrategy 클래스
export class RandomStrategy implements Strategy {
private won: boolean = true;
private prevHand: Hand;
public nextHand = (): Hand => {
this.prevHand = Hand.getHand(Math.floor(Math.random() * 3));
return this.prevHand;
};
public study = (win: boolean): void => {
this.won = win;
};
}
RandomStrategy 클래스 또한 Strategy 인터페이스를 구현하는 클래스 중 하나이다.
이 클래스는 직전 승부와 관계없이 랜덤으로 손을 낸다는 전략을 취한다.
Player 클래스
export class Player {
private name: string;
private strategy: Strategy;
private winCount: number = 0;
private loseCount: number = 0;
private gameCount: number = 0;
constructor(name: string, strategy: Strategy) {
this.name = name;
this.strategy = strategy;
}
public nextHand = (): Hand => {
return this.strategy.nextHand();
};
public win = (): void => {
this.strategy.study(true);
this.winCount++;
this.gameCount++;
};
public lose = (): void => {
this.strategy.study(false);
this.loseCount++;
this.gameCount++;
};
public even = (): void => {
this.gameCount++;
};
public toString = (): string => {
return `[${this.name} : ${this.gameCount} game, ${this.winCount} win, ${this.loseCount} lose ]`;
};
}
Player 클래스는 가위바위보를 하는 사람을 표현한 클래스이며, "이름", "전략"이 할당되어 인스턴스를 생성한다.
nextHand 메소드는 다음의 손을 얻기 위한 것이지만, 실제로 다음의 손을 결정하는 것은 자신의 전략이다.
전략의 nextHand 메소드의 반환값이 그대로 Player의 nextHand 메소드의 반환값이 되는, 즉 위임하고 있다.
이기거나, 지거나, 비기거나한 승부의 결과를 다음 승부에 활용하기 위해서 Player 클래스는 strategy 필드를 통해 study 메소드를 호출한다.
study 메소드를 사용해서 전략의 내부 상태를 변화시킨다.
Main 메소드
const main = () => {
const player1: Player = new Player('하나', new WinningStrategy());
const player2: Player = new Player('두리', new RandomStrategy());
for (let i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
const nextHand1: Hand = player1.nextHand();
const nextHand2: Hand = player2.nextHand();
if (nextHand1.isStrongerThan(nextHand2)) {
console.log(`Winner: ${player1}`);
player1.win();
player2.lose();
} else if (nextHand2.isStrongerThan(nextHand1)) {
console.log(`Winner: ${player2}`);
player1.lose();
player2.win();
} else {
console.log('Even');
player1.even();
player2.even();
}
}
console.log('Total Result : ');
console.log(player1.toString());
console.log(player2.toString());
};
main();
main 메소드는 앞의 클래스를 이용해서 실제로 컴퓨터에서 가위바위보를 실행하기 위한 메소드이다.
WinningStrategy 전략을 사용하는 '하나', RandomStrategy 전략을 사용한 '두리'가 10번 대전시켜 그 결과를 표시한다.
실행 예시
Winner: [하나 : 0 game, 0 win, 0 lose ]
Winner: [하나 : 1 game, 1 win, 0 lose ]
Winner: [두리 : 2 game, 0 win, 2 lose ]
Winner: [하나 : 3 game, 2 win, 1 lose ]
Even
Even
Even
Winner: [두리 : 7 game, 1 win, 3 lose ]
Winner: [하나 : 8 game, 3 win, 2 lose ]
Winner: [두리 : 9 game, 2 win, 4 lose ]
Total Result :
[하나 : 10 game, 4 win, 3 lose ]
[두리 : 10 game, 3 win, 4 lose ]
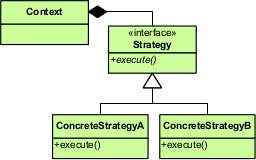
Strategy 패턴의 구성요소
-
Strategy
Strategy는 전략을 이용하기 위한 인터페이스를 결정한다. 예제 프로그램에서는
Strategy인터페이스가 담당하였다. -
ConcreteStrategy
위 Strategy 인터페이스를 구현한다. 여기에서 구체적인 전략을 실제로 개발하며, 예제 프로그램에서는
WinningStrategy클래스와RandomStrategy클래스가 담당하였다. -
Context
Context는 Strategy를 이용하는 역할을 한다. ConcreteStrategy의 인스턴스를 가지고 있으며 필요에 따라 그것을 사용한다. 예제 프로그램에서는
Player클래스가 담당하였다.
일부러 Strategy 역할을 만들 필요가 있을까 ?
Strategy 패턴에서는 알고리즘의 부분을 다른 부분과 의식적으로 분리해서 알고리즘의 인터페이스 부분만을 규정하고 위임에 의해 알고리즘을 이용한다.
더욱이 위임이라는 느슨한 연결을 사용하고 있으므로 알고리즘을 용이하게 교환할 수 있다.
예를 들어 알고리즘을 개량해서 사용하고 싶을 때, Strategy 패턴을 사용하면 Strategy 역할의 인터페이스를 변경하지 않도록 주의하고 ConcreteStrategy 역할만을 수정하면 된다. 원래의 알고리즘과 개량 알고리즘의 속도를 비교하고 싶은 경우에도 간단하게 교체해서 시험할 수 있다.
실행 중에 교체도 가능
Strategy 패턴을 사용하면 프로그램의 동작 중에 ConcreteStrategy 역할의 클래스를 교체할 수 있다.
예를 들어, 메모리가 적은 환경에서는 SlowButLesttMemoryStrategy를 사용하고, 메모리가 많은 환경에서는 FastButMoreMemoryStrategy를 사용하는 것도 생각할 수 있다.
다른 예로 한쪽의 알고리즘을 다른 쪽 알고리즘의 '검산'에 이용할 수도 있다. '버그가 있을지도 모르는 고속의 알고리즘'과 '저속이지만 확실한 계산을 실행하는 알고리즘'이 있을 때 전자의 검산을 후자로 실행하는 것이다.
관련 패턴
-
Flyweight
ConcreteStrategy 역할은 Flyweight 패턴을 사용해서 복수의 장소에서 공유할 수도 있다.
-
Abstract Factory
-
State
Strategy 패턴, State 패턴 둘 다 위임하는 곳을 교환하는 패턴이고 클래스 간의 관계도 매우 비슷하지만 목적이 다르다.
Strategy 패턴은 '알고리즘'을 표현하는 클래스를 작성해서 해당 클래스를 교체할 수 있지만 필요하지 않으면 교체하지 않아도 된다. 하지만 State 패턴에서는 '상태'를 표현하는 클래스를 작성해서 해당 클래스를 상태가 변화할 때마다 위임하는 곳의 클래스가 반드시 교체된다.